What is cybersecurity?
In simplest terms, cybersecurity is how individuals and organisations reduce and subsequently eliminate the risk of a cyber attack.
What are the functions of cybersecurity?
Cyber security’s core function is to protect the online services we all access, either at home or at work, from hack, theft and damage. It is also referred in terms of protecting all our digital devices, be it computers, tablets, and smartphones, from unauthorised access to the vast amounts of personal information we store on these devices, and online.
Why is cybersecurity important?
Even before Covid-19 struck, cybersecurity was a very important – but sadly often ignored – part of an individual’s and company’s day-to-day functioning.
This so as the cyber world (commonly referred to as the internet), smartphones and computers, are now a fundamental part of modern life. From online shopping to banking, to emails and social media, to now working from home using app like Zoom, Meet or Skype, cyber world is as much a part of our lives now as the real world. That’s why it is increasingly important to prevent cyber criminals from getting hold of our accounts, data, and devices. Often these cyber attacks are aimed at interrupting normal business processes, extorting money, or accessing and destroying sensitive information.
That’s why cybersecurity is important. As in today’s connected world, everyone benefits from having installed advanced cyberdefense mechanisms and programs.
At an individual level, you are protected against identity theft, and extortion attempts. At a company level, you are protected against loss of sensitive information and disruption in normal business flow. At a government level, critical infrastructure such as power plants, hospitals, and financial services are secured.
What are the types of cybersecurity threats a company faces these days? Most commonly, these are as under:
-
Social engineering – This is a tactic that attack on confidentiality. It is the process of psychologically manipulating and tricking people into revealing sensitive information. The attackers can then extort money or sell your data to your competitors.
Phishing attacks are the most common form of social engineering. Phishing attacks usually come in the form of a deceptive email with the goal of tricking the recipient into giving away personal information.
-
Malware – This is a tactic that attack on availability. It refers to software that is designed to gain access to your digital devices or network without your knowledge. Once inside, the malware can steal your login information, or use your computer to send spam or crash the entire network. Several common types of malware include spyware, keyloggers, true viruses, and worms.
From a company’s perspective, Ransomware, are the most common form of malware. As depicted in the name itself, a Ransomware aims to lock and encrypt your computer or device data—essentially holding your files hostage—and then demand a ransom to restore access. Common types of ransomware include crypto malware, lockers and scareware.
-
APTs (Advanced Persistent Threats) – This is a tactic that attack on integrity. Here, an unauthorized user infiltrates a network undetected and stays in the network for a long time. The aim of an APT is to steal data, and such a cyberattack is often found in sensitive and critical sectors such as national defense, manufacturing, and the finance industry.
Now to the most important part of this article.
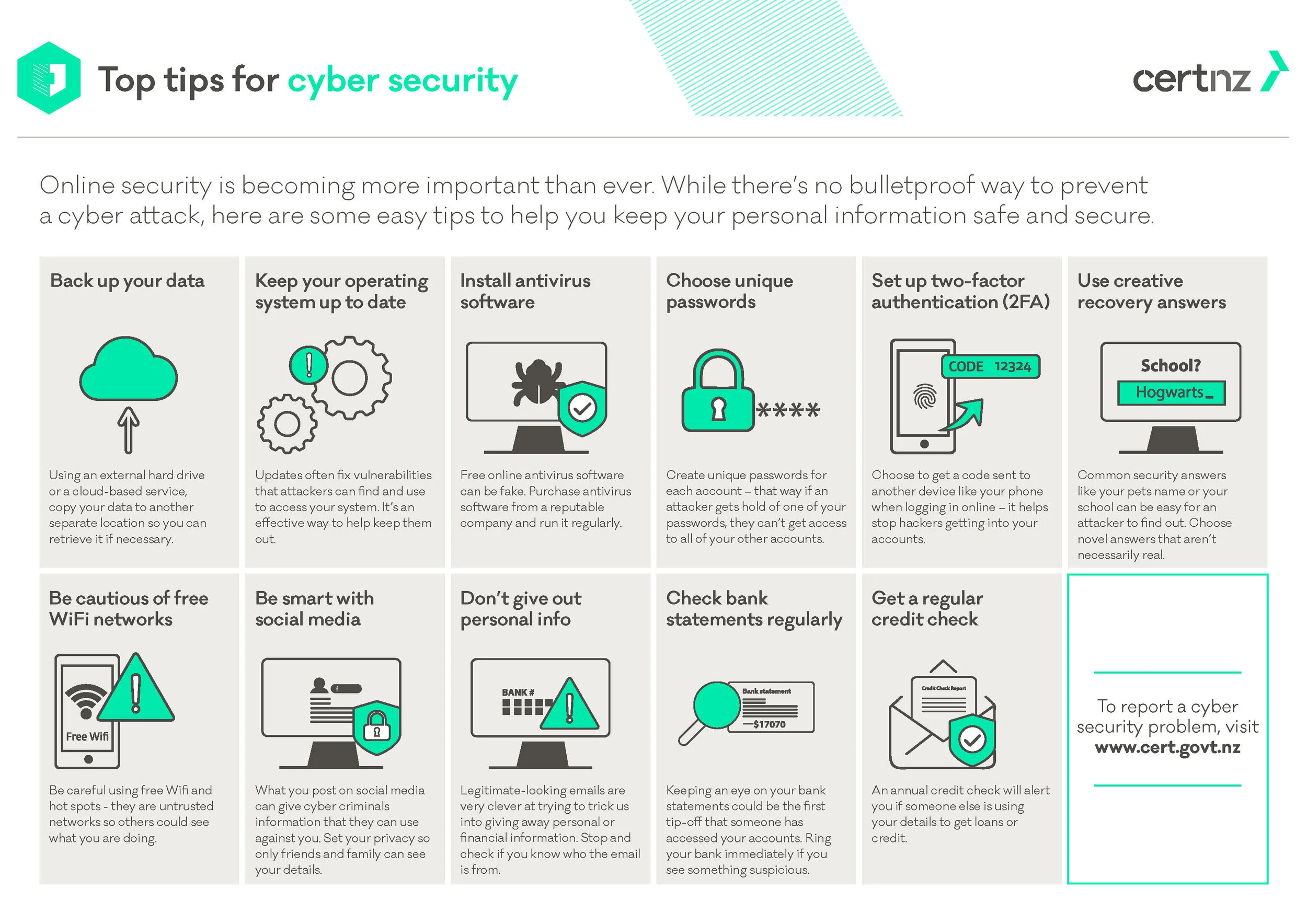
13 tips for a company to improve cybersecurity
To minimize the risks of cyberattacks, a company – and every individual for that matter – must follow the following 13 basic cybersecurity best practices, at least.
1) Install a firewall
A firewall may be able to block malicious traffic before it can enter a computer or a network system. Some device operating systems already include a firewall. So it’s advisable to enable and properly configure the firewall as specified in the device or system owner’s manual.
2) Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA)
A MFA uses at least two identity components to authenticate a user’s identity, minimizing the risk of a cyberattacker gaining access to an account if they know the username and password. An example of this is a two-factor authentication (2FA), under which you can choose to have a code sent or generated on your device, like your phone, that you can use to authenticate who you are every time you log in. That way, even if someone gets access to the account password, if they don’t have your phone to receive the code they can’t get into your accounts.
3) Be suspicious of unexpected emails
As mentioned above, phishing emails are currently one of the most prevalent risks to the average user. So always be suspicious of all unexpected emails.
4) Don’t open email attachments/links from unknown sources
One of the most common ways networks and users are exposed to malware and viruses is through emails disguised as being sent by someone you trust. So don’t open any such sends.
5) Use strong passwords
This is plain common sense. Always select passwords that will be difficult for attackers to guess, and use different passwords for different programs and devices. It is best to use long, strong passphrases or passwords that consist of at least 16 characters.
6) Only use trusted sites when providing your personal information
A good rule of thumb is to check the URL. If the site includes “https://,” then it’s a secure site. If anything else, avoid entering sensitive information like your credit card data.
7) Back up your files
Regularly back up your network or computer, for extra protection in the event of a cyber security attacks. If you need to wipe your device clean due to a cyberattack, it will help to have your files stored in a safe, separate place.
8) Be creative with your account recovery questions
When you set up a new account online, you’re often asked to set an answer to few account recovery question. A general advise is to be creative with your answers so that these are not easy for hackers to guess or find and gain access to your accounts without your knowledge.
9) Run up-to-date antivirus software
A reputable antivirus software application is an important protective measure against known malicious threats. But make sure to enable automatic virus definition updates to ensure maximum protection against the latest threats.
10) Keep software up-to-date
Install software patches so that attackers cannot take advantage of known problems or vulnerabilities. Enable the automatic updates that many operating systems provide these days.
11) Be careful when using public wifi
It’s good to be careful about what you do online when you’re using a hotspot or free wifi as these networks are often unsecure. Here, you are often at risk of people shoulder surfing.
12) Be smart about social media
Check the privacy controls on your social media accounts, and set them so only your friends and family can see your full account details. As a general rule, don’t put too much personal information on your social media accounts.
13) Stay informed
Finally, always remember, cyber security is constantly evolving, which can make it difficult to stay up to date. Staying informed and being cautious online are two of the best ways to help protect yourself, your networks and devices, and your business.
All the above information is courtesy www.cert.govt.nz, www.us-cert.gov, and www.ncsc.gov.uk
– TIN Bureau